Chop the herb up

place it in an empty bottle no more than ¾ full.

Put that in the freezer, with the lid off.
Place a bottle of 95% Ethanol in the freezer too.

12-24 hrs later…
The herb should be frozen solid….

Pour the freezing cold ethanol into the bottle of frozen herb until covered by ¼ to a 1/3 over the top of the herb, put the lid on tight and shake for 3 min. The ethanol will change colour from clear to Gold or Amber. No more than 3 minutes. Work swiftly, you do not want to see any hint of a green colour.
3 Minute shake

Stop.
Remove lid and strain.
First through a piece of cheesecloth over the top of the bottle.

Or,, a standard kitchen strainer

Next, pour through a coffee filter paper, set into a kitchen funnel, with the bottom of the funnel directed into the capture bottle.
Be patient,,,,,,, it will take its own sweet time to get through the coffee paper. Do not try to force it through.
Rinse
Pour a small amount of freezing cold Ethanol to flush the last bit out of the coffee filter.
When it drips out clear, no color. Your done, you got it all.
Cannabis Tincture
The result is a red/yellow off-clear, full strength Tincture of Cannabis.
With little to no chlorophyll’s to speak of and all three medicinal fractions fully rinsed from the herb.
Evaporate the Ethanol out.
Non Activated Extract
Use a fan in a well ventilated area. this process will deliver a non-active cannabinolic acid extract eg THCA, CBDA, etc..
Non-Active extracts are not psycho active,, that means you don’t get stoned, or high from non active extracts.
or
Activated Extract
For fully activated extracts THC CBD. Apply gentle heat, below 100c. Use a rice cooker or steamer, well ventilated area eg.. outdoors, or Simply
pour into a baking tray and leave, outdoors, in the full, direct sunlight.
The dry oil is amber-clear, and highly potent.
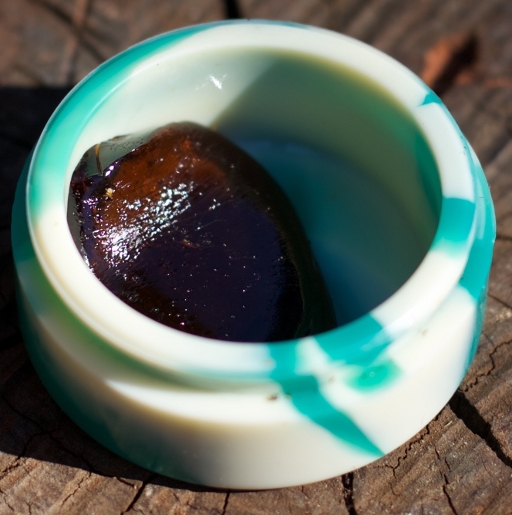
Hash Oil
Full strength medical cannabis extract is a three-part synergy of cannabinoids, terpenoids and flavi(o)noids.
Extractions for medical use should take up all three medicinal families with great efficiency and minimize the amount of chlorophyll’s, concrete oils and waxes which have minimal therapeutic value.
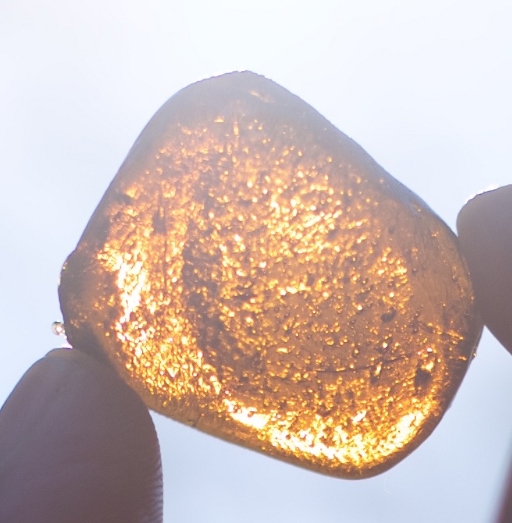 hash oil
hash oil
Where to find 95% medicinal grade Ethanol.

A.K.B. Productions Pty Ltd.
Lot 60 Deepwater Road.
Torrington. N.S.W. 2371
ph/fax 02, 67346322
or
Polmos Spirytus Rectified Spirit 95% 500mL
You get it from the local bottle shop. They may have to order it in for you.
Or
Buy it online.







